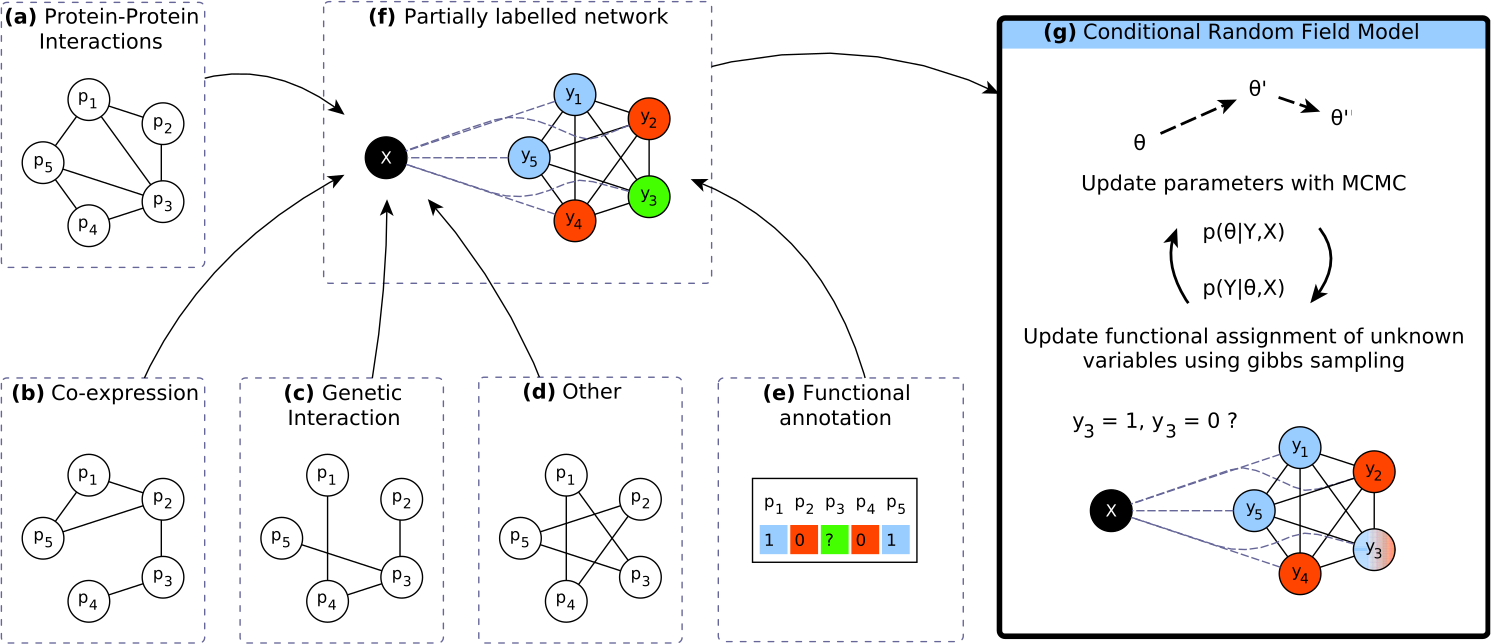

Introduction Markov Random Fields (MRF) have been shown to be good predictors of functional annotation, using protein-protein interaction data. Many other sources of data can also be used in this prediction task, but they are typically not integrated.In this study, we extend a method using MRFs in order to allow the use of additional data.
Results A conditional random field (CRF) model is proposed as an alternative to an MRF model in order to remove the requirement of modeling relationships between the sources of data. We observe that a substantial performance improvement is possible using additional data, such as genetic interaction networks. The improvement gained from each source of evidence is not the same for each protein function, indicating that each source supplies different information. We demonstrate that CRFs can be used to efficiently integrate various sources of data to predict functional annotations.